
Batching—whether in concrete production, food processing, or pharmaceuticals—is the process of measuring and mixing raw materials in precise quantities before production. The goal is to ensure consistency, efficiency, and quality in the final product. But does batching really lead to higher accuracy, or are there cases where it could introduce errors?

What is Batching in Manufacturing?
Batching is the process of measuring and combining materials in specific proportions before they undergo production. Unlike continuous manufacturing, where production happens non-stop, batching follows a step-by-step approach, ensuring controlled and precise ingredient mixing.
Batching vs. Continuous Production: Key Differences
| Feature | Batching Production | Continuous Production |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Materials are processed in set batches. | Materials flow continuously without stops. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to controlled measuring and mixing. | Can have variations due to real-time material fluctuations. |
| Flexibility | Can adjust batch formulas easily. | Harder to make mid-process changes. |
| Quality Control | Each batch can be tested before proceeding. | Harder to check quality in real-time. |
| Best For | Concrete, food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals. | Oil refining, paper production, steel manufacturing. |
Batching is widely used in industries where precise ingredient ratios are critical to product quality. Some common applications include:
- Concrete Batching Plants: Mixing cement, water, sand, and aggregates in precise ratios for strong and durable concrete.
- Food & Beverage Manufacturing: Ensuring recipes maintain consistency in taste, texture, and safety.
- Pharmaceuticals & Chemicals: Measuring active ingredients with extreme accuracy to meet safety standards.
Batching plants play a crucial role in automating and standardizing this process. But how exactly do they work?
How Do Batching Plants Work?
A batching plant is a centralized facility designed to measure, mix, and deliver materials in predefined quantities. These plants use advanced weighing systems, automated controls, and real-time monitoring to ensure accuracy.
Key Components of a Batching Plant
- Weighing Systems – Measures raw materials like cement, sand, water, and additives with extreme precision.
- Mixing Unit – Combines materials in controlled proportions to achieve uniform consistency.
- Storage Bins/Silos – Hold raw materials before they enter the batching process.
- Conveyor Belts – Transport materials to the mixing unit.
- Control Systems (SCADA & PLCs) – Automate the batching process, ensuring every batch meets set standards.
- Moisture Sensors – Adjust water content in real time to maintain material consistency.
How a Concrete Batching Plant Works: Step-by-Step
- Raw Material Loading: Cement, aggregates, water, and additives are stored in silos.
- Weighing & Measurement: Each material is precisely weighed using automated scales.
- Mixing Process: The materials are transferred to a mixer where they are blended to ensure even distribution.
- Quality Control: Sensors check for moisture, consistency, and air content.
- Batch Delivery: The final mix is sent to transport vehicles or directly used in production.
Modern batching plants rely heavily on automation to reduce human error and improve accuracy. But is batching always the best choice for accuracy? Let’s explore how it impacts precision in manufacturing.
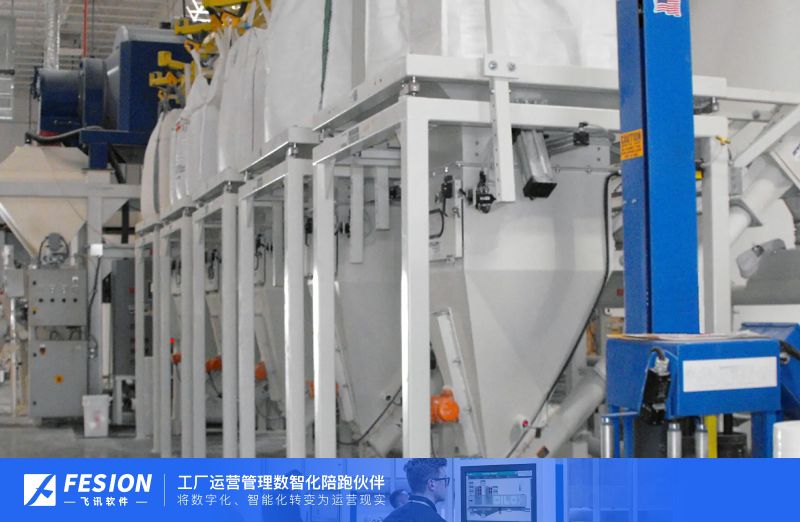

How Does Batching Impact Accuracy in Manufacturing?
When it comes to precision in manufacturing, batching has a significant impact on product consistency, material usage, and overall quality control. But does batching improve accuracy across all industries? Let’s break it down.
1. The Role of Batching in Ensuring Measurement Accuracy
Accuracy in manufacturing starts with precise measurement of raw materials. Batching plants use weighing systems, load cells, and volumetric measurements to ensure the right proportions are maintained in every batch. This is especially critical in industries like concrete production, where even minor variations in cement-to-water ratios can affect the strength and durability of the final product.
For example, in concrete manufacturing:
- The ideal water-cement ratio for high-strength concrete is 0.4 to 0.6.
- A 1% deviation in water content can reduce concrete strength by up to 10%.
This highlights how even small errors in measurement can lead to weaker structures, increased costs, and potential safety risks. Batching plants use automated sensors and real-time monitoring to minimize such deviations, ensuring the mix remains within optimal parameters.
2. Accuracy in Mixing and Homogeneity
Batching is not just about measurement; it’s also about evenly mixing materials to achieve a consistent final product. Uneven mixing can cause:
- Segregation – Some components settle at the bottom, while others stay at the top.
- Inconsistent Strength – Some parts of the batch might be weaker than others.
- Wastage – Poorly mixed batches may need to be discarded or reprocessed.
Batching plants address this by using high-speed mixers, agitation tanks, and rotation-based mixing techniques to ensure uniformity.
3. Quality Control and Defect Reduction
Batching allows manufacturers to test and validate each batch before production continues, making it easier to catch defects early. Unlike continuous production—where flaws may go unnoticed until large amounts of defective products are made—batching gives manufacturers a checkpoint to review quality before moving forward.
Case Study: How Batching Improved Accuracy in Concrete Production
A 2019 study by the National Ready Mixed Concrete Association (NRMCA) analyzed batching accuracy across 50 concrete plants. The results showed:
- Plants with automated batching had a 95% accuracy rate in material measurements.
- Manually controlled plants had a 78% accuracy rate, leading to higher variability in concrete strength.
- Automated batching reduced material wastage by 12%, cutting costs and improving sustainability.
This demonstrates that batching—when automated and well-maintained—can significantly improve accuracy in manufacturing.
4. Comparing Batching vs. Continuous Production for Accuracy
Does batching always lead to better accuracy? Not necessarily. In some cases, continuous production methods may be more reliable, especially when dealing with high-volume, low-variability products.
| Factor | Batching | Continuous Production |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy Control | Higher, due to precise measurement per batch | Can be harder to maintain consistency |
| Defect Detection | Easier to catch issues before large-scale production | Issues may go undetected for longer |
| Material Wastage | Less waste due to controlled portions | Potential for more waste in case of process errors |
| Flexibility | Easy to adjust formulas per batch | Harder to change formulas mid-process |
| Speed | Can be slower due to stop/start nature | More efficient for mass production |
For industries like concrete, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, batching is preferred due to its ability to ensure accuracy, control variations, and maintain strict quality standards. However, for industries like oil refining and paper manufacturing, continuous production may be more efficient, as long as real-time monitoring systems are in place.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Batching for Accuracy
Batching is widely used in manufacturing because of its ability to enhance precision, control quality, and reduce material waste. However, it’s not a perfect system. While it provides strong control over accuracy, there are also limitations that manufacturers need to consider.
Let’s take a closer look at the key benefits and drawbacks of batching in manufacturing.
Advantages of Batching for Accuracy
1. Higher Measurement Precision
One of the biggest advantages of batching is its ability to precisely measure materials before production. Unlike continuous production—where materials flow non-stop and minor deviations can accumulate—batching ensures that every batch follows an exact formula.
✅ Example: In concrete production, batching plants use load cells and automated weighing systems to ensure the correct water-to-cement ratio, which directly impacts compressive strength and durability.
✅ Fact: A 1% error in cement proportioning can reduce the final concrete strength by 5-10%, highlighting the need for accurate batching.
2. Better Quality Control and Defect Reduction
Because batching processes materials in set amounts, it allows manufacturers to test and validate each batch before moving forward. This prevents large-scale defects that might go undetected in continuous production.
✅ Example: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, batch testing ensures that each drug formulation meets safety and potency standards before being distributed. If a batch fails quality checks, it can be discarded or reworked without affecting the entire production line.
✅ Industry Data: The FDA requires batch testing for pharmaceuticals to maintain accuracy in drug composition, ensuring that every dose is within ±2% of the labeled potency.
3. Reduced Material Waste
Batching minimizes waste by ensuring that only the required materials are used in each batch. This is particularly beneficial in industries where raw materials are expensive, such as chemicals, construction materials, and food production.
✅ Example: A concrete batching plant that automates material measurements can reduce cement overuse by 5-7%, leading to lower costs and reduced environmental impact.
4. More Flexibility in Production
Batching allows manufacturers to adjust formulations easily without disrupting the entire production process. This is especially useful for industries that need to produce multiple product variations.
✅ Example: A food manufacturing plant that makes sauces can use batching to easily adjust ingredient ratios for different flavors, ensuring accuracy while maintaining production efficiency.
Disadvantages of Batching for Accuracy
While batching improves accuracy in many ways, there are also challenges that manufacturers need to address.
1. Slower Production Speed
Because batching works in a stop-and-start manner, it can be slower than continuous production, which operates without interruptions.
⚠️ Example: In high-demand industries like automotive manufacturing, a continuous production line can assemble vehicles at a faster rate compared to batch production methods.
⚠️ Solution: To reduce downtime, some manufacturers use hybrid batching systems, where certain processes (like material weighing) happen in parallel with production.
2. Potential for Material Segregation
If materials are not properly mixed, batching can lead to inconsistent product quality due to material separation. This is a common issue in industries that handle powders, granules, or liquids.
⚠️ Example: In concrete production, improper batching can cause aggregate segregation, leading to weak spots in the final structure.
⚠️ Solution: Advanced batching plants use continuous agitation and real-time sensors to prevent material separation and ensure homogeneity.
3. Requires Frequent Calibration and Maintenance
To maintain accuracy, batching plants need regular calibration and maintenance of their weighing and mixing systems. Failure to do this can lead to:
- Inaccurate material measurements
- Inconsistent batch quality
- Increased material wastage
⚠️ Example: A concrete plant with uncalibrated load cells can overdose or underdose cement, leading to weaker structures.
⚠️ Solution: Implementing scheduled calibration and preventive maintenance ensures batching systems remain accurate over time.
4. Delayed Feedback on Errors
Unlike continuous production—where errors can be detected in real time—batching relies on post-production testing. This means that if a mistake occurs, it may not be noticed until an entire batch is completed.
⚠️ Example: In pharmaceutical production, if an incorrect dosage is detected after a batch is processed, the entire batch must be discarded, resulting in financial losses.
⚠️ Solution: Some manufacturers integrate real-time monitoring and AI-driven quality control to detect errors as early as possible.
Is Batching the Best Choice for Accuracy?
Batching is an excellent method for improving accuracy in industries where precise measurement and quality control are critical. However, it requires proper automation, regular calibration, and effective mixing techniques to prevent errors.
Pros & Cons of Batching for Accuracy
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✅ High measurement precision | ⚠️ Slower production speeds |
| ✅ Improved quality control | ⚠️ Risk of material segregation |
| ✅ Reduces material waste | ⚠️ Requires frequent calibration |
| ✅ Allows flexibility in production | ⚠️ Delayed error detection |
When to Use Batching for Accuracy
✅ Best for industries that require precise formulations (e.g., concrete, pharmaceuticals, food production).
✅ Ideal for high-value materials where waste reduction is important.
✅ Necessary when flexibility and quality control are more critical than speed.
🚫 Less suitable for industries that prioritize mass production speed over precision.